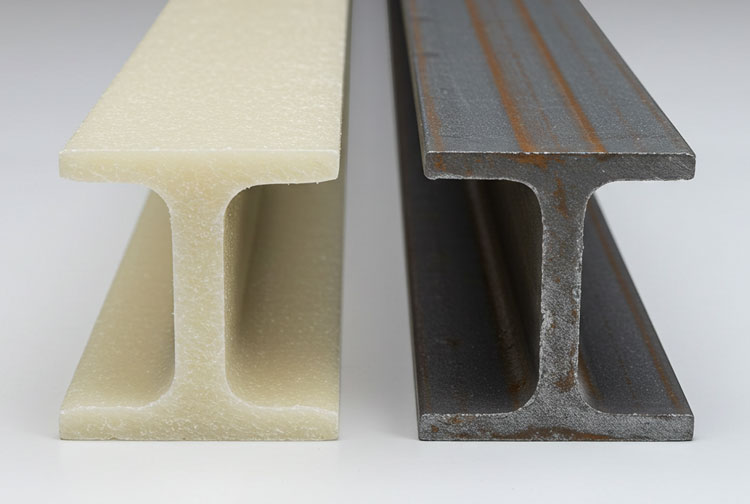
Fiberglass beams vs steel beams
The choice of materials for structural elements, such as beams, can significantly impact the overall performance and longevity of a building. Two popular options for beams are fiberglass and steel. Both materials offer unique properties and advantages, making them suitable for different applications. In this article, we will delve into the key differences between fiberglass beams and steel beams, helping you make an informed decision for your construction project.
Fiberglass Beams
Fiberglass beams are composite materials composed of fiberglass fibers embedded in a resin matrix. They offer several advantages over traditional steel beams:
Corrosion Resistance: Fiberglass beams are highly resistant to corrosion, making them ideal for environments exposed to moisture, chemicals, or saltwater.
Lightweight: Fiberglass beams are significantly lighter than steel beams, reducing transportation and installation costs.
High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Fiberglass beams offer excellent strength-to-weight ratios, making them suitable for applications where weight is a critical factor.
Electrical Insulation: Fiberglass is a non-conductive material, making it ideal for electrical applications or environments where electrical conductivity is a concern.
Dimensional Stability: Fiberglass beams are dimensionally stable, meaning they are less likely to warp or twist over time.
Customizability: Fiberglass beams can be custom-engineered to meet specific load requirements and design specifications.
Steel Beams
Steel beams have long been the industry standard for construction due to their high strength and durability. However, they also have certain limitations:
Corrosion: Steel is susceptible to corrosion, especially in environments with high humidity or exposure to chemicals.
Weight: Steel beams are relatively heavy, which can increase transportation and installation costs.
Electrical Conductivity: Steel is an excellent conductor of electricity, which can be a concern in certain applications.
Fiberglass Beams vs. Steel Beams: A Comparison
| Feature | Fiberglass Beams | Steel Beams |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Susceptible to corrosion |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavy |
| Strength | High strength-to-weight ratio | High strength |
| Electrical Conductivity | Non-conductive | Conductive |
| Dimensional Stability | Excellent | Can warp or twist over time |
| Cost | Generally higher upfront cost | Lower upfront cost |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low | High |
Applications of Fiberglass Beams
Fiberglass beams are well-suited for a wide range of applications, including:
Marine industry: Fiberglass beams are used in boat building, docks, and other marine structures due to their corrosion resistance and lightweight properties.
Chemical processing plants: Fiberglass beams are used in environments exposed to corrosive chemicals, such as tanks, platforms, and walkways.
Infrastructure: Fiberglass beams are used in bridges, overpasses, and other infrastructure projects due to their durability and lightweight.
Sports facilities: Fiberglass beams are used in the construction of sports arenas, stadiums, and gymnasiums.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Fiberglass and Steel Beams
Environmental conditions: If corrosion is a concern, fiberglass beams are the better choice.
Load-bearing requirements: For heavy loads, steel beams may be more suitable.
Budget: Fiberglass beams may have a higher upfront cost but can offer long-term savings due to their durability and low maintenance requirements.
Aesthetic considerations: Fiberglass beams can be customized to match various aesthetic requirements.
Installation complexity: Fiberglass beams are generally easier to install due to their lightweight nature.
Conclusion
The choice between fiberglass and steel beams depends on a variety of factors, including the specific application, environmental conditions, and budget constraints. Fiberglass beams offer a compelling alternative to steel beams, providing exceptional corrosion resistance, lightweight properties, and versatility. By carefully considering the unique properties of each material, engineers and architects can make informed decisions to select the most suitable beam material for their projects.
Additional Considerations:
Fire resistance: Both fiberglass and steel beams have fire resistance properties, but the specific performance can vary depending on the type of resin used in the fiberglass and the thickness of the steel.
Thermal conductivity: Fiberglass beams have lower thermal conductivity than steel beams, making them suitable for applications where thermal insulation is important.
Sustainability: Both fiberglass and steel beams have environmental impacts. Consider the sourcing of materials and the end-of-life disposal options when making a decision.
By understanding the pros and cons of both fiberglass and steel beams, engineers and architects can make informed decisions that optimize the performance and longevity of their structures.
 +86 15303735673
+86 15303735673 Jessica@frpzs.com
Jessica@frpzs.com
 Technical Data
Technical Data











